PowerShell Library for HPE Compute Ops Management
After long months of hard work, I am excited to announce the release of my new PowerShell library for HPE Compute Ops Management. This comprehensive library offers a robust set of cmdlets designed to manage and automate your HPE GreenLake environment efficiently. By leveraging this library, users can seamlessly interact with HPE GreenLake and Compute Ops Management services directly from the PowerShell command line, integrating effortlessly into existing automation workflows.
Development is ongoing, and my efforts are far from finished. As we all know, SaaS cloud applications evolve over time. Therefore, this library will be continuously updated to incorporate new features as they are released by HPE.
This module is available in the PowerShell Gallery under the name HPECOMCmdlets, following the naming convention used by most HPE modules.
The PowerShell Gallery is a repository for sharing and distributing PowerShell modules and scripts. It’s a community-driven platform that provides access to various PowerShell resources, enabling you to easily discover, install, and publish your own PowerShell content. The PowerShell Gallery can be accessed through the PowerShellGet module (includes Install-Module, Find-Module, etc.), which comes pre-installed with Windows PowerShell 5.0 and above.
This project is also associated with a new repository on my GitHub account. This repository is where the source code is developed. You can also track releases, report and view issues, and participate in discussions.
Key Features
This library provides a variety of key features for managing HPE GreenLake and Compute Ops Management. Here are the main features:
- Authentication: Establish secure connections to HPE GreenLake using Single Sign-On (SSO) or single/multi-factor authentication. Whether you have an existing workspace or not, the library supports flexible authentication methods to suit your needs.
- Workspace Management: Create and manage HPE GreenLake workspaces.
- Session Tracking: Automatically track sessions with the global session tracker
$HPEGreenLakeSession. - User Management: Invite and manage users within your HPE GreenLake environment, assign roles.
- Resource Management: Manage resources such as servers, storage, and networking within your HPE GreenLake environment.
- Service Provisioning: Provision services like Compute Ops Management, manage service roles and subscriptions.
- Device Management: Add devices individually or in bulk using CSV files, manage device subscriptions and auto-subscriptions, set device locations and connect devices to services.
- Server configuration Management: Create and apply BIOS, storage, OS, and firmware settings. Manager group and apply configurations to groups of servers.
- Security and Compliance: Manage iLO security settings and run inventory and compliance checks.
- Job Scheduling and Execution: Schedule and execute various tasks like firmware updates, OS installations, and sustainability reports.
- Notification and Integration: Enable email notifications for service events and summaries, integrate with external services like ServiceNow.
- Appliance Management: Add HPE OneView and Secure Gateway appliances, upgrade HPE OneView appliances.
- Monitoring and Alerts: Monitor alerts for your resources to ensure optimal performance and uptime.
- Reporting: Generate detailed reports on resource usage, performance, and other metrics.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks and workflows using PowerShell scripts and cmdlets.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrate with other tools and platforms using REST APIs and webhooks.
- Security: Implement security best practices and manage access control for your HPE GreenLake environment.
These features collectively provide a comprehensive set of cmdlets to manage various aspects of your HPE GreenLake environment and any existing Compute Ops Management service instances.
Requirements
For detailed system requirements and prerequisites, please refer to the README.md file in the GitHub repository.
Installation
To install the library, use the following command to download and install the module from the official PowerShell Gallery:
Install-Module HPECOMCmdlets
Note: As a best practice, always install the newest release to get all the latest features and fixes.
If this is your first time installing a module from the PowerShell Gallery, you will be prompted to confirm whether you trust the repository. Type Y and press Enter to proceed.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Internet Connection: An active internet connection is required to install the module from the PowerShell Gallery.
- No Dependencies: This library has no external dependencies, so no additional software or modules are required for it to function.
- Common Issues:
-
Insufficient Permissions: If you encounter permission issues, run PowerShell as an administrator or use the
-Scope CurrentUserparameter:Install-Module HPECOMCmdlets -Scope CurrentUser -
Execution Policy Restrictions: If the execution policy is set to
Restricted, it may block the installation. Check your current policy using:Get-ExecutionPolicyIf it returns
Restricted, update it toRemoteSigned:Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSignedWarning: Changing the execution policy affects the security of your system. Ensure you understand the implications before proceeding.
-
By following these steps, you can successfully install the HPECOMCmdlets module and begin using it in your PowerShell 7 environment.
How to Upgrade the Module
If you have already installed the module and need to update it to the latest version, run the following commands:
Install-Module -Name HPECOMCmdlets -Force -AllowClobber
Note: If you encounter permission issues during the upgrade process, run PowerShell as an administrator or use the
-Scope CurrentUserparameter with theInstall-Modulecmdlet.
Getting Started
Using Single or Multi-Factor Authentication
To connect using single or multi-factor authentication, follow these steps:
-
Single-Factor Authentication:
Use the following command to connect with your email and password:
Connect-HPEGL -Credential (Get-Credential) -Workspace "YourWorkspaceName"-
Note: If you do not have a workspace yet, omit the
-Workspaceparameter. You can create a new workspace after your first connection using theNew-HPEGLWorkspacecmdlet. -
Note: The
-Credentialparameter is optional. If omitted, the module will prompt you to enter your username and password interactively. -
Tip: Unsure of the workspace name? Connect without specifying the
-Workspaceparameter, then runGet-HPEGLWorkspaceto list all available workspaces. Once identified, useConnect-HPEGLWorkspace -Name "YourWorkspaceName"to connect to the desired workspace.
-
-
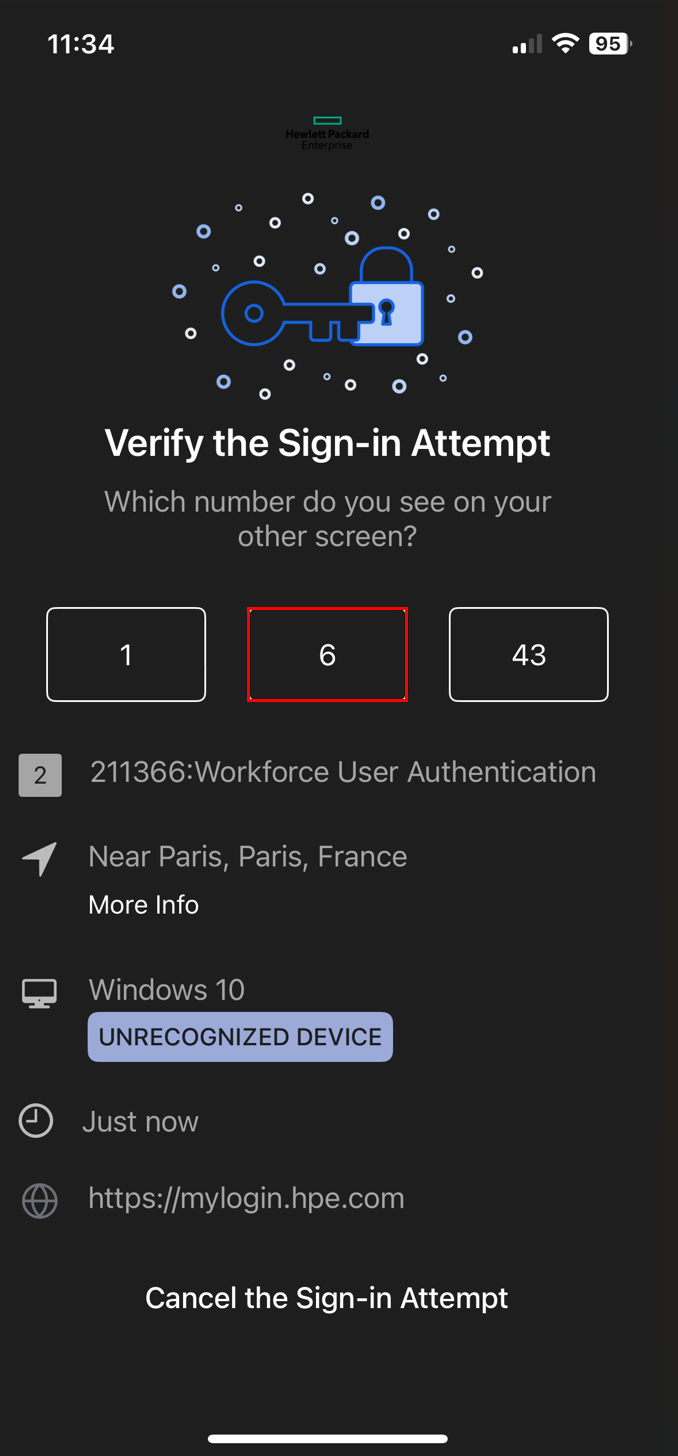
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
The library supports Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) using Google Authenticator or Okta Verify. Before proceeding, ensure the appropriate app is installed on your device and linked to your account. For detailed guidance on setting up and using MFA with HPE GreenLake, refer to the Multifactor Authentication Guide.
-
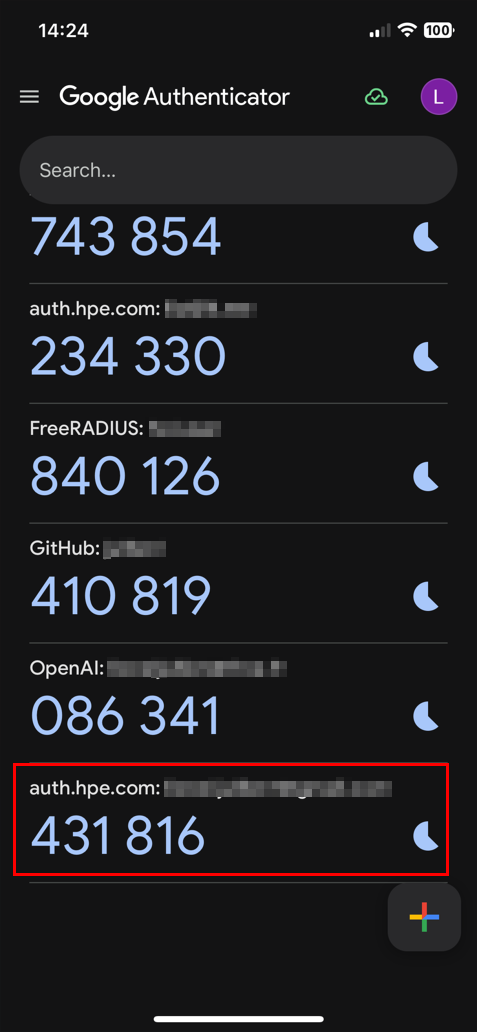
For accounts with Google Authenticator, you will be prompted to enter the verification code.
-
For accounts with Okta Verify, approve the push notification on your mobile device.
-
If both are enabled, the library defaults to Okta Verify.
Use the same command as above to connect using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Connect-HPEGL -Credential (Get-Credential) -Workspace "YourWorkspaceName"Note: MFA with security keys or biometric authenticators is not supported. If your account is configured for these methods only, enable Google Authenticator or Okta Verify in your account settings.
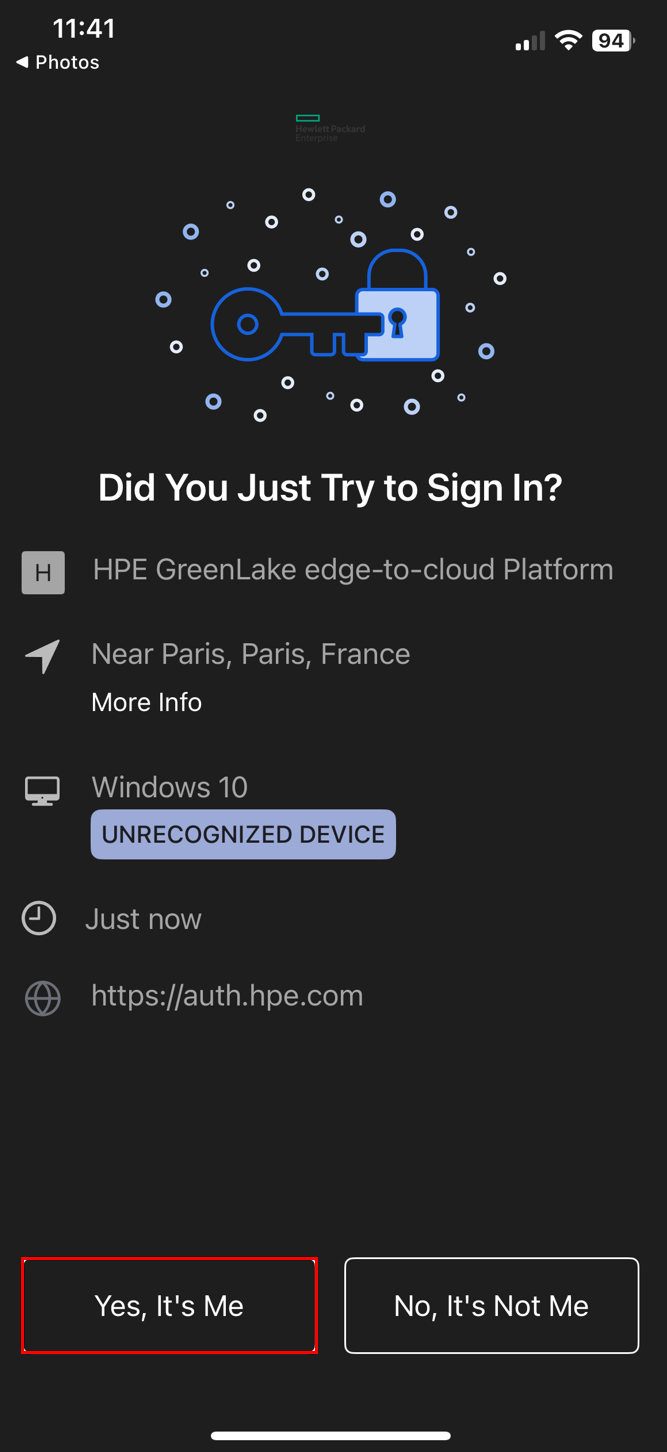
- When MFA is enabled with Okta:
- When MFA is enabled with Google Authenticator:
-
Using SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) with Okta
The library provides support for SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) exclusively with Okta. To ensure a successful authentication process, follow these steps:
- Install and Configure Okta Verify:
-
Download and install the Okta Verify app on your device.
-
Link your Okta account to the app by following the setup instructions provided by your organization.
-
- Authentication Process:
-
Use the following command to connect using SAML SSO with Okta:
Connect-HPEGL -SSOEmail "firstname.lastname@domain.com" -Workspace "YourWorkspaceName" -
If you do not have a workspace yet, omit the
-Workspaceparameter. You can create a new workspace after your first connection using theNew-HPEGLWorkspacecmdlet.
-
- Validation:
- Tips:
- Unsure of the workspace name? Connect without specifying the
-Workspaceparameter, then runGet-HPEGLWorkspaceto list all available workspaces. Once identified, useConnect-HPEGLWorkspace -Name "YourWorkspaceName"to connect to the desired workspace.
- Unsure of the workspace name? Connect without specifying the
For detailed guidance on setting up and using SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) with HPE GreenLake, refer to the Authentication Guide.
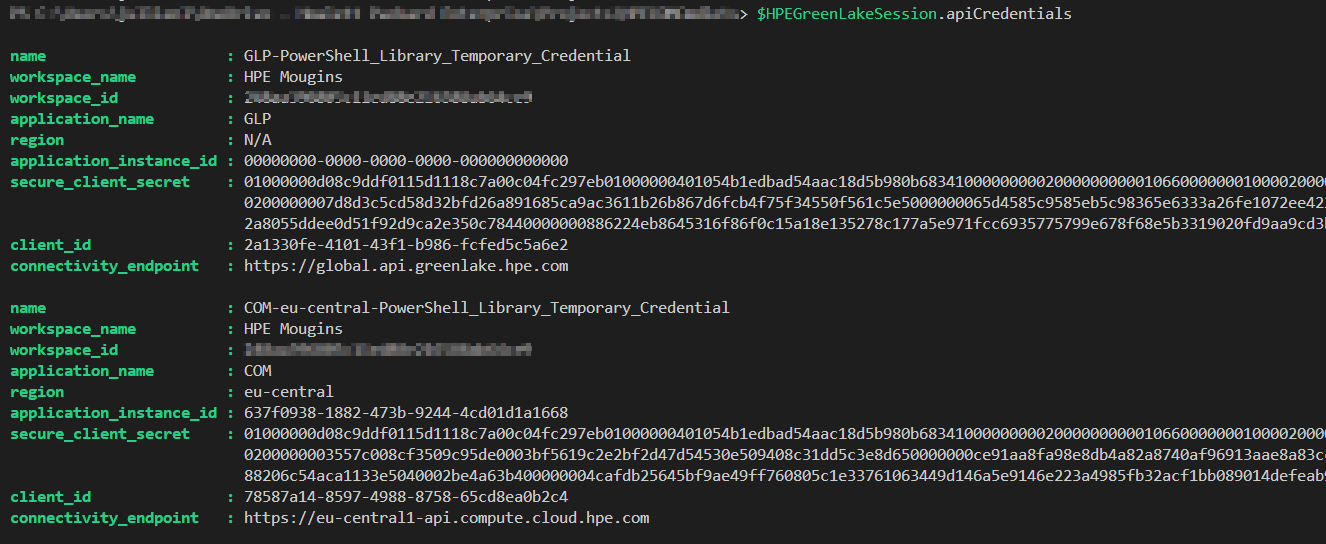
Global Session Object: $HPEGreenLakeSession
Upon successful connection, the Connect-HPEGL cmdlet returns:
- A persistent session that is used for all subsequent cmdlet requests within the module.
- Temporary API client credentials for both HPE GreenLake and any Compute Ops Management service instances provisioned in the workspace.
- A global session object stored in the
$HPEGreenLakeSessionvariable, which contains session details, API client credentials, access tokens, and other relevant information for interacting with HPE GreenLake and Compute Ops Management APIs.
Key Properties of $HPEGreenLakeSession:
- Access Tokens: Temporary tokens used for authenticating API requests.
- Workspace Details: Information about the connected HPE GreenLake workspace.
- Session Expiry: The expiration time of the current session.
- API Client Credentials: Credentials used for API interactions.
- User Information: Details about the authenticated user.
Usage Example:
To view the details of the $HPEGreenLakeSession object, simply run:
$HPEGreenLakeSession
This will display all the properties and their current values.
Managing Sessions:
- To disconnect and clear the session, use the
Disconnect-HPEGLcmdlet. - To refresh an expired session, re-run the
Connect-HPEGLcmdlet with the appropriate credentials.
For more details, refer to the help documentation of the Connect-HPEGL cmdlet:
Get-Help Connect-HPEGL -Full
Script Samples
To help you get started quickly, I have provided a sample script.
This file contains a variety of examples demonstrating how to use the different cmdlets available in the library to accomplish various tasks.
With HPE GreenLake:
- Setting up credentials and connecting to HPE GreenLake
- Configuring workspace, inviting new users and assigning roles
- Provisioning services and managing device subscriptions
- Adding devices individually or via CSV files
With HPE Compute Ops Management:
- Creating BIOS, internal storage, OS, and firmware settings.
- Managing group and adding servers to groups.
- Running inventory jobs and setting auto firmware updates.
- Powering on servers and updating firmware.
- Applying configurations and installing OS on servers.
- Generating sustainability reports and enabling email notifications.
- Adding external services like ServiceNow.
- Managing and upgrading HPE OneView and Secure Gateway appliances.
Feel free to modify and expand upon these examples to suit your specific needs. This file is an excellent starting point for understanding the capabilities of the module and how to leverage it in your automation workflows.
Getting help
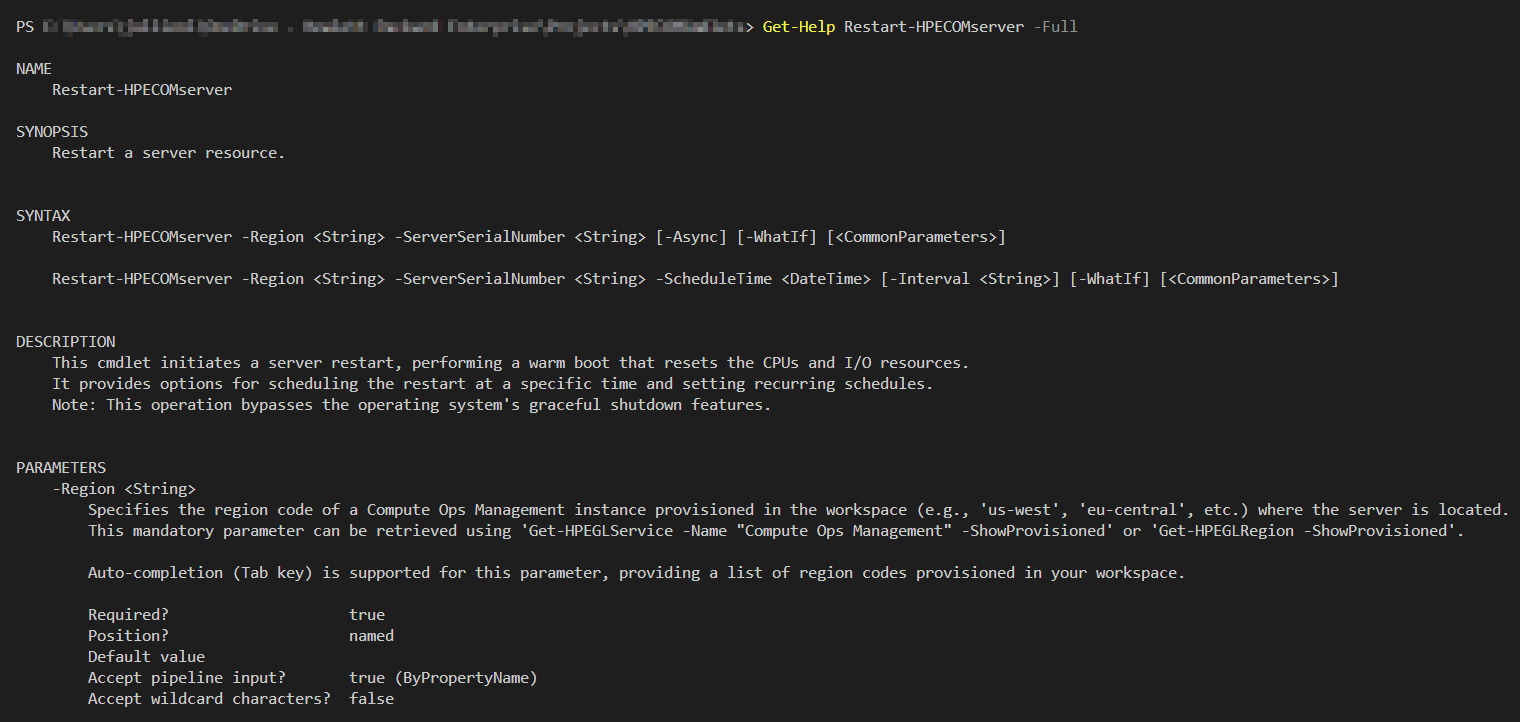
For more detailed information on each cmdlet and its usage, refer to the module’s help documentation using:
Get-Help <CmdletName> -full
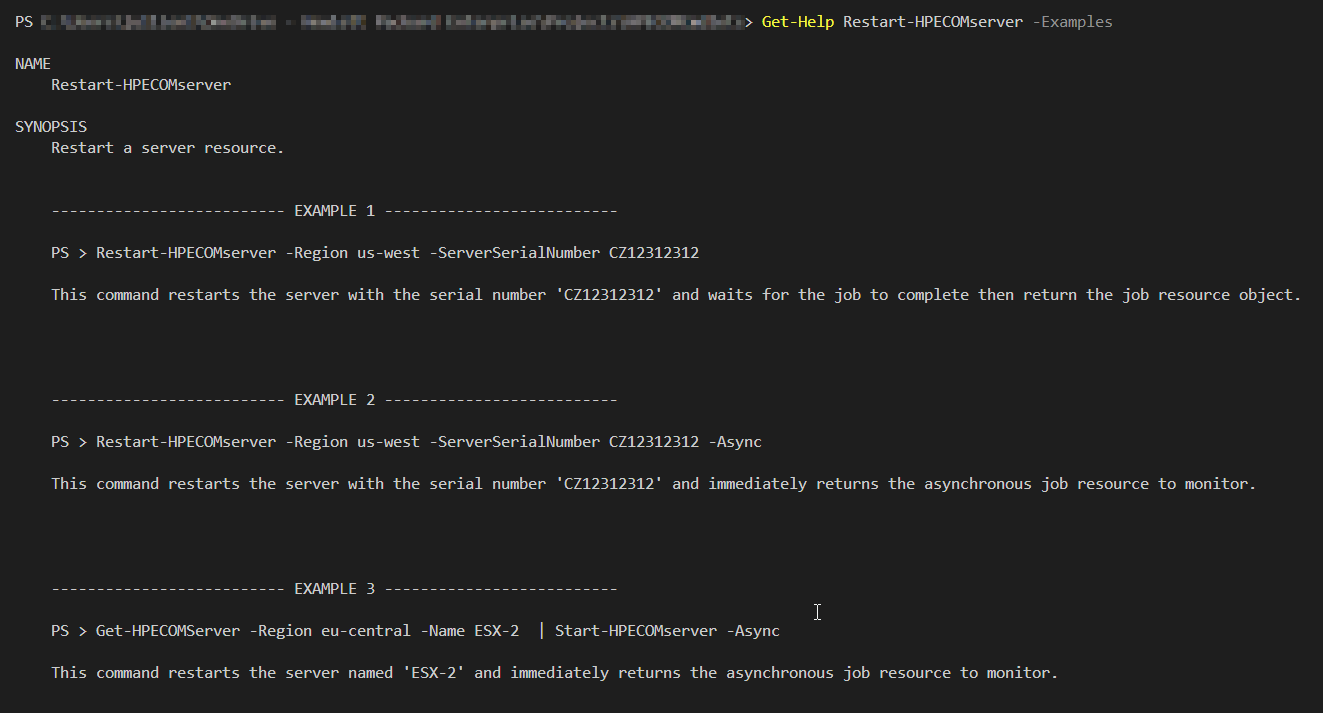
To see detailed examples of how to use a specific cmdlet, use the Get-Help cmdlet with the -Examples parameter followed by the cmdlet name.
Get-Help <CmdletName> -Examples
To list all commands exported by the module, use:
Get-Command -Module HPECOMCmdlets
To find cmdlets related to a specific resource, use:
Get-Command -Module HPECOMCmdlets | ? Name -match "<ResourceName>"
# Example
Get-Command -Module HPECOMCmdlets | ? Name -match group
Support
If you encounter any issues or unexpected behavior, please open a new issue on my GitHub issue tracker for assistance.
For general questions or discussions that don’t require tracking, join our GitHub Discussions.
Disclaimer
Please note that the HPE GreenLake APIs are subject to change. Such changes can impact the functionality of this library. We recommend keeping the library updated to the latest version to ensure compatibility with the latest API changes.
Want more?
your hub for all HPE software-related content!